Pure, strong vitamin K2 dissolved in olive oil
- Pure vitamin K2 (Menaquinone MK-7) dissolved in cold-pressed olive oil
- 100% recommended daily allowance (RDA)
- Supports the maintenance of normal bones and normal blood coagulation
- Small, soft gelatin capsules that are easy to swallow
- Manufactured under pharmaceutical control
K-Pearls 60 pcs
| 1 capsule contains: | %NRV* | |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin K2 | 75ug | 100% |
* NRV: Nutrient Reference Value.
Product facts
Directions:
1 capsule per day for adults and children 11 years and older. The capsule can be chewed or swallowed whole.
Do not exceed recommended amount.
Dietary supplements should not be used as a substitute for a varied diet or healthy lifestyle.
Pregnant and lactating women and those on medication should seek professional advice prior to taking supplements.
Ingredients:
Bulking agent: Olive oil (Cold-pressed)
Capsule shell: Bovine gelatine
Humectant: Glycerol, purifed water
Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone)
Colour: Iron oxide
Storage:
Room temperature out of direct sunlight. Keep out of reach of children.
Shelf life:
Minimum 2 years.
 K-Pearls contains small, soft gelatin capsules with 75 μg of pure vitamin K2 (menaquinon MK-7) in each capsule. The vitamin K2 is dissolved in cold-pressed olive oil for improved absorption of the nutrient. The capsules are easy to swallow because of their size, and they can also be chewed. Take K-Pearls with a meal.
K-Pearls contains small, soft gelatin capsules with 75 μg of pure vitamin K2 (menaquinon MK-7) in each capsule. The vitamin K2 is dissolved in cold-pressed olive oil for improved absorption of the nutrient. The capsules are easy to swallow because of their size, and they can also be chewed. Take K-Pearls with a meal.
All-Trans MK-7
In nature, vitamin K is found in a trans form and a cis form. The individual form relates to the spatial structure of the molecule. It is only the trans form of MK-7 that is biologically active. The cis form has no biological activity. K-Pearls is an all-trans form and is therefore biologically active.
What is vitamin K?
Vitamin K belongs to the group of lipid-soluble vitamins that also includes with vitamins A, D, and E.
Vitamin K was discovered by the Danish biochemist Henrik Dam in 1929. In 1943, he was awarded a Nobel Prize for his discovery. The vitamin was named vitamin K with K standing for "koagulation", the Danish and German term for coagulation. Later, it was discovered that there are two main types of vitamin K: phylloquinone (K1) and menaquinone (K2). In addition, there is a synthetic version of vitamin K called menadione (K3), which is normally not used in dietary supplements.
Vitamin K2 is found in various forms, ranging from MK-4 to MK-14. MK-10 and higher forms of the vitamin, however, rarely occur. The MK number refers to the length of the vitamin's side chain of so-called isoprene units. MK-7 and MK-4 are normally the forms used in nutritional supplements.
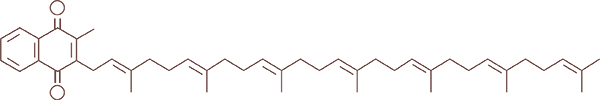
Why vitamin K2 MK-7?
Vitamin K2 MK-7 stays longer in the body than both vitamin K1 and vitamin K2 MK-4. Therefore, the MK-7 version is thought to be more effective. Both K1 and K2 MK-4 are metabolized and excreted rapidly in the body, and we have only a small amount of stored vitamin K in the liver, spleen, and lungs.
Vitamin K and bones
Vitamin K2 is particularly important for the distribution of calcium to our bone tissue. Our bone tissue is broken down and reconstructed in a continuous cycle. Our age, activity level, and diet affect the process. This becomes increasingly important when we grow older, because after the age of 30-35 years, we start to lose bone mass. We can slow down the process by making the right lifestyle choices. It is especially vitamin K2 that supports the transport of calcium into the bone tissue. The bone-forming cells are called osteoblasts. They produce a protein called osteocalcin that is activated by vitamin K. This activation is important for the transport of calcium from the blood and blood vessels and the process of embedding calcium into the bone tissue to support normal bone function.
Vitamin K and coagulation
Vitamin K is also a necessary factor in the intricate coagulation process. Vitamin K is necessary for the formation of prothrombin and various coagulation factors called coagulation factor VII, coagulation factor IX, and coagulation factor X.
What does vitamin K2 do?
Vitamin K2 has an essential role in keeping calcium 'mobile' in the body (and it does this by activating various proteins). Vitamin K dependent proteins can help ensure ideal calcium placement in the body (into bones, not into blood vessels). Calcium deposited into bones can contribute to bone health and structure, whereas calcium deposited into blood vessels can contribute to calcification - a hardening of the arteries associated with various cardiovascular health issues.
Variations in gelatin hardness
The hardness of our soft gelatin capsules can vary. The difference depends solely on the water content of the capsule shell. We dry all our soft capsules before packaging, which makes the capsules firmer and facilitates the packaging process itself. Over time, the capsules can absorb water from the air, and this will soften the capsule shell.
The variations in the hardness of the capsule have no effect on the product quality, but if a hard capsule is a problem, a solution may be to leave the capsule outside the blister sheet for a day, whereby the capsule can absorb a little water from the air. This is generally not something we recommend, as the product will no longer be protected as when it is in the blister sheet. Another method of quickly softening the gelatin capsule is to place it in lukewarm water for one minute. However, it should be seen as an emergency solution.
Vitamin K2 Benefits
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the evidence behind vitamin K and has acknowledged the following claims:
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal bones
- Contributes to normal blood clotting


