Add images for the product gallery inside the div with red border. Remove the height and width when inserting the images
Set Alternative text for images
Add iframe with a youtube link, Iframes require a image thumbnail as the next sibling as well.
Connect iframe and iframe thumbnail sibling with id on the elements,
like so :
On iframe id="iframe1",
On iframe thumbnail image : id="iframe1thumbnail"
Add Long Description
Highly soluble and absorbable magnesium complex
- Bio-Magnesium contains a complex of three different magnesium salts in a matrix to ensure rapid dissolution and good absorption
- Supports the maintenance of normal bone and teeth.
- Contributes to normal nerve function and normal muscle contractions
- Contributes to reduced fatique
- Manufactured under Danish pharmaceutical control
- Please note that this is a Dutch package.
Bio-Magnesium
| 1 tablet contains: | % RDA* | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | 200 mg | 53% |
* RDA = Recommended Daily Allowance
Product Facts
Directions
1 tablet daily, unless otherwise advised.
Do not exceed the recommended daily dosage.
You can swallow the tablet whole or dissolve it in a glass of water. You do not need to take the tablet with a meal.
Dietary supplements should not replace a varied diet.
A healthy lifestyle and a varied diet are important for maintaining good health.
Suitable for vegetarians.
Ingredients
Magnesium carbonate
Magnesium hydroxide
Magnesium acetate
Bulking agent: Microcrystalline cellulose
Anti-caking agent: Dicalcium phosphate
Glazing agent: Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
Anti-caking agent: Magnesium salts of fatty acids
Firming agent: Silicon dioxide
Storage
Dark, dry and at room temperature.
Keep out of reach of young children.
What is Bio-Magnesium?

Bio-Magnesium is a complex of three different magnesium salts. Each tablet provides you with 200 mg of pure magnesium. The tablet contains a mixture of organically and inorganically bound magnesium contained in a matrix that enables the tablet to dissolve completely within minutes - even in the digestive systems of people with low stomach acid.
Bio-Magnesium tablets are normally swallowed whole but they can also be chewed or dissolved in a glass of water. It is not necessary to take Bio-Magnesium with a meal.
Documented effect
Magnesium test
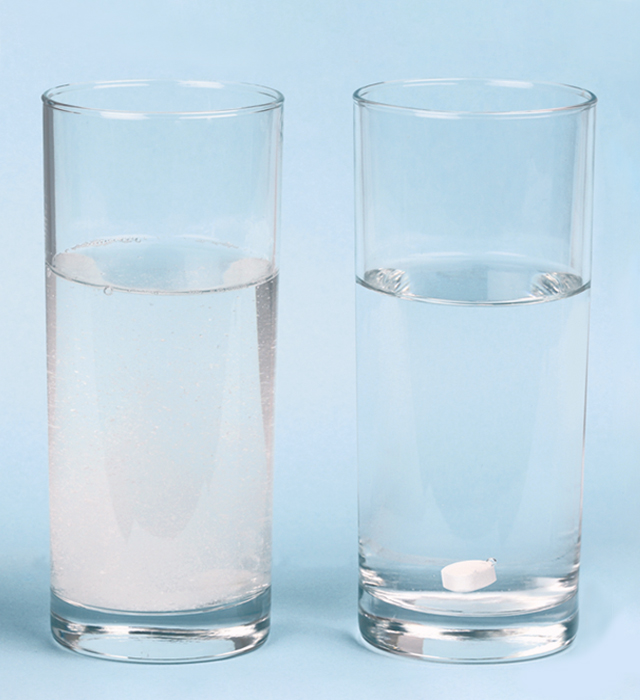 You can easily test if your magnesium tablet dissolves properly. We have placed two magnesium tablets in separate glasses of water. In the left glass, the Bio-Magnesium tablet from Pharma Nord has dissolved completely within minutes and can be absorbed by the body. The glass to the right contains a competing magnesium brand. Even after being submerged in water for more than 24 hours the tablet is unaffected and has not dissolved the least bit.
You can easily test if your magnesium tablet dissolves properly. We have placed two magnesium tablets in separate glasses of water. In the left glass, the Bio-Magnesium tablet from Pharma Nord has dissolved completely within minutes and can be absorbed by the body. The glass to the right contains a competing magnesium brand. Even after being submerged in water for more than 24 hours the tablet is unaffected and has not dissolved the least bit.
Documented bioavailability
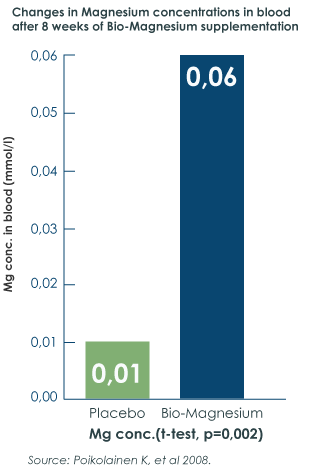
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study from 2008, participants who had been taking Bio-Magnesium daily for eight weeks had six times higher blood levels of magnesium than the participants in the control group that been taking a placebo pill.
What is magnesium?
Magnesium is an essential mineral and a vital alkaline-forming element. Also, it is the fourth most abundant mineral in the human body which says something about its importance. Magnesium is present in all our cells, with 98% of the mineral being inside the actual cell and only two percent outside the cell. An adult contains approximately 24 grams of magnesium. About 25% is found in muscle tissue and about 60% is in our bones together with other minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
Magnesium has several important roles in the body. It supports more than 300 different enzyme processes that are important for things such as:
- Normal muscle function
- Normal energy metabolism
- Maintenance of normal bones and teeth
- Normal psychological functions and electrolyte balance
- Normal functioning of the nervous system
- A reduction of tiredness and fatique
- Normal protein synthesis
- The process of cell division
Increased focus on magnesium
Science has become increasingly interested in magnesium because of the mineral’s widespread role in so many different body functions. Certain factors can increase the need for magnesium. Excessive intake of coffee and alcohol is known to deplete magneisum levels in the body, and elite athletes also need extra magnesium because heavy sweating depletes the body's magnesium stores.
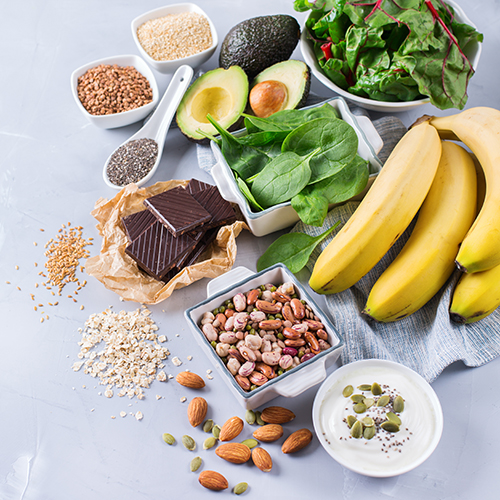 Good magnesium sources
Good magnesium sources
Magnesium is found in different foods with some of the best sources being:
- Nuts
- Almonds
- Leafy greens
- Seeds
- Oats
- Kale
There is even some magnesium in water, but the content varies and is only able to cover a limited part of our needs. Especially bottled water may contain only very small amounts of magnesium.
Magnesium deficiency
Low dietary intake of protein (less than 30 g per day) reduces the body’s magnesium absorption. In situations where the body lacks magnesium, it attempts to maintain a normal magnesium concentration in the blood by releasing magnesium that is bound in bone tissue (it does the same with calcium). Because of this rather intricate mechanism, measuring blood levels of magnesium is not necessarily a useful way to determine if a person needs more magnesium.
Unhealthy diets tend to cause a magnesium loss, just like the body's magnesium reserves are drained by alcohol abuse, hard physical activity, and stress.
Overdosing
Our kidneys excrete magnesium in the urine if we get more magnesium than our body needs. This mechanism conveniently reduces the risk of getting too much. Once the body's magnesium requirement is met, additional intake of magnesium will result in loose bowels. This is another protective mechanism against overdosing. Magnesium intake in extremely high doses (10 times the normal dosage or more) may cause diarrhea, nausea, and other types of discomfort.
Individuals with renal impairment should not take supplements of magnesium unless advised by a physician.
Official claims
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the evidence behind magnesium and has acknowledged the following claims:
- Contributes to the maintenance of normal bones and teeth
- Contributes to normal functioning of the nervous system
- Contributes to normal muscle function, energy-yielding metabolism, and psychological functions
- Contributes to electrolyte balance
- Contributes to the normal protein synthesis
- Contributes to a reduction of tiresness and fatigue
Related Products
 Vitamin D has several sites in common with magnesium: For example, both contribute to the maintenance of normal bones and teeth, a normal muscle function. Also they both play a role in cell division.
Vitamin D has several sites in common with magnesium: For example, both contribute to the maintenance of normal bones and teeth, a normal muscle function. Also they both play a role in cell division.